Cheese, prunes, and farm supplies such as hay, straw, corn, rapeseed, flour and dry food for pets may contain many mites. The mites are only present when the goods are damp. The storage mites only occur only in products where microorganisms – in the form of bacteria and fungi – are already present in huge numbers.
Itchy skin
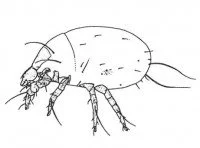
When handling mite-infected goods, you can get an itchy rash on the skin, especially on the hands and forearms. The rash is attributed to the mites. However, one must keep in mind that storage mites are relatively large – up to 1/2 mm long, so it’s usually the ones you see when you examine an item. Therefore, it is far from certain that mites are the cause of the itching skin. It might as well be the microorganisms and the aggressive chemical environment they form around them.
Many different mites
The most common mite in cheese is the cheese mite, Tyrolichus casei, which is found in cracks in the cheese. On the surface of dried fruit, a fruit mite, Carpoglypus lactis, is found. In the other goods, the mite fauna is dominated by the genus Acarus, Lepidoglyphus, Tyrophagus and, especially in hay, Tydeus and Tarsonemus.
The storage mites mainly feed on the microorganisms in the goods. One of the exceptions is a predatory mite, Cheyletus eruditus, which attacks the other storage mites and sucks them dry. It is closely related to fur mites and can be confused with them. It injects its digestive enzymes into the prey and – perhaps – they can do the same to human skin.
Allergies
Many people develop allergies of storage mites in the surrounding environments. Symptoms may include itching of the eyes and nose, rhinitis or asthma attacks every time you are exposed to dust from mite-infected goods. Especially people who work in the agricultural sector are afflicted by the mite-infected dust. The mite that most often cause allergic reactions is the Lepidoglyphus destructor – one of the most common mites in stored grain, hay and straw. Here, ecological recovery is not the solution. You can protect yourself with breathing masks, get vaccinated against the storage mites or take medication, which relieve the symptoms. The alternative is to change profession.




