Ectoparasites in humans, dogs, cats, rabbits and guinea pigs.
Ectoparasites in Humans
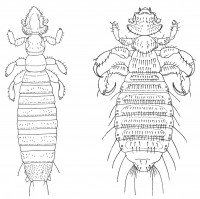
The human louse, Pediculus humanus. P.19. The louse sucks blood through contact. There are two species of human lice: the head louse, Pediculus humanus capitis, which lives in the scalp hair and the body louse, Phcorporis, which lives on the body and clothes.
The crab louse, Phthirus pubis. P.3. The crab louse sucks blood and lives in the body hair of humans, especially on the abdomen. The crab louse is transmitted by intimate contact.
The bed bug, Cimex lectularius. P.41. The bed bug feed on human blood, which they suck from us at night. They are found in heated homes and are transmitted when infested house hold effect are moved.
The human flea, Pulex irritans. P.92. It is found in moist, dirty houses. It sucks blood from humans. It is rare and is transmitted by transfer of adult fleas and when moving infested household effects.
There are two species of follicle mites, Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis. P.123. They live in hair follicles, especially on the nose, feed on sebum and rarely causes symptoms. They are transmitted by body contact.
The itch mite, Sarcoptes scabiei. P.115. The itch mites feed on the top layer of the skin. They are especially found between fingers and on wrists. The itch mites are transmitted by intimate contact.
Ectoparasites in Dogs
The dog louse, Linognathus setosus. P.35. It is especially found on the head, neck and back of the dog where it feeds on blood. Are similar to the human louse, however, it does not have any eyes like the human louse. Does not infect humans.
The dog’s biting louse, Trichodectes canis, sometimes known as the canine chewing louse. P.36.It chews on the dog’s skin, mostly on the head, ears and neck. It has a broad head. Cannot infect humans and does not bite humans.
Dog flea, Ctenocephalides canis. P.96. Feeds on blood, and is similar to the cat flea. Nowadays, dog fleas are quite rare. They are controlled like cat fleas. Will bite humans when given the opportunity. Cannot infect cats.
Cat Flea, Ctenocephalides felis. P.96. It is a very common, blood sucking flea and the cat flea is especially common in the late summer. It bites humans. The fleas are transmitted between dogs and cats and both functions as host animals.
The brown dog tick, Rhipicephalus sanguineus. P.107. Is a large blood sucking mite, which is imported from warmer countries. It can bite humans, however it is rare.
Canine nasal mites, Pneumonyssus caninum. P.126. It has a yellowish-white color, is up to 1.5 mm long, and it lives in the nasal cavities and sinuses of dogs. It is usually not seen and is harmless for the dogs and humans. Does not infect humans.
The dog fur mite, Cheyletiella yasguri. P.128. It feeds on the top layer of the skin and can cause severe itching in both dogs as well as humans. It cannot live on humans.
The dog follicle mite, Demodex canis. P.124. It feeds on the sebum of all dogs, and can multiply violently in some sick dogs. It does not infect humans.
The dog’s itch mite, Sarcoptes scabiei. P.122. Feeds on the top layer of the skin, causing thickening of the skin and itching with dogs. The dog’s itch mite can infect humans, however, it only causes mild symptoms.
The ear mite, Otodectes cynotis. P.125. It chews the skin inside the auditory canal. It lives in the auditory canals of the dog as well as in the fur near the ears. The ear mite causes itching in the ears and ear infection. It is transmitted between dogs and cats but is harmless to humans.
Ectoparasites in Cats
Cat lice, Felicola subrostrata. P.36. Feeds on the skin of the head, neck and back of the cat. Normally, without discomfort to the cat. Does not bother humans. Cats have no blood sucking lice.
Cat flea, Ctenocephalides felis. P.96. The cat flea sucks blood. The same species are seen in dogs and transmits between dogs and cats. It will bite people when given the opportunity. The larvae live in carpets and in the cat’s sleeping place.
Cat fur mite, Cheyletiella blakei. P.128. Feeds on the top layer of the skin. Cats are usually asymptomatic. When in contact with humans, it can bite. It is not transmittable to dogs.
Cat follicle mite, Demodex cati. P.123. The follicle mites in cat feed of sebum rarely causes symptoms in cats and cannot be transmitted to humans or dogs.
The cat itch mite, Sarcoptes scabiei. P.122. Feeds on the top layer of the skin, causing thickening of the skin as well as itching. Humans can be infected, however, the symptoms are mild.
The small notoedric mite, Notoedres cati, P.xx. Its way of life is similar to that of the cat itch mite. Can possibly infect dogs, but probably not humans. This species of mites is rare.
Cat ear mite, Otodectes cynotis. P.125. Same species and symptoms as the dog ear mite. Can transmit between dogs and cats.
Ectoparasites in Rabbits
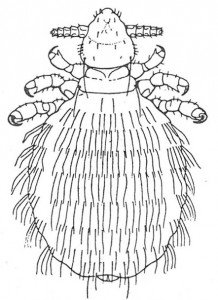
Rabbit louse, Haemodipsus ventricosus. It sucks the blood of its host animal. Is up to 2 1/2 mm long, and causes itching. This mite does not infect humans. Rabbits do not have biting lice.
Rabbit Flea, Spilopsyllus cuniculi. It is a rather small, blood sucking flea and is found in groups on the inside of the ears of, preferably in wild rabbits. The rabbit flea may bite people. It is a vector for a contagious, fatal infection in rabbits.
Rabbit fur mite, Cheyletiella parasitovorax, P.128. Feeds on the top layer of the skin and possibly on other mites. It rarely causes symptoms in the host rabbits. It is common and can bite humans.
Rabbit follicle mite, Demodex cuniculi. Feed on the sebum and usually causes no symptoms. It does not infect humans.
Rabbit itch mite, Sarcoptes scabiei. P.122. Feed on the top layer of the skin, forming burrows in the skin on the head and legs. It causes thickening of the skin, itching and hair loss in rabbits. It causes mild symptoms in humans.
The small notoedric mite in rabbits, Notoedres cuniculi. It feeds on the top layer of the skin, especially on the nose, head and genitals. I causes itching, thickening of the skin and hair loss. Does not infect humans.
Rabbit ear mite, Psoroptes cuniculi. Is found in the auditory canal, where it chews on the top layer of the skin. It causes itching and rash inside the ear. It does not infect humans.
Listrophorus gibbus. A mite that feeds on sebum, etc., found in the coat on the entire body. It is common and harmless to both rabbits and humans.
Ectoparasites in Guinea Pigs
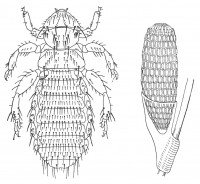
Trimenopon jenningsi. A biting louse. It is 1.7 mm long and seen throughout the body of the guinea pig. It causes itching and does not infect humans.
Gliricola Porcelli. Another species of the biting louse. It is up to 1.7 mm long and very thin. It is found throughout the body, causing itching and hair loss. Harmless to humans.
Gyropus ovalis. A third species of the biting louse. It only 1 mm long, and is found on the neck as well as on the back of the head. It causes itching and dull fur. It does not infect humans.

The guinea pig itch mite, Sarcoptes scabiei. P.122. Symptoms include thickened skin and itching. It can transfer pseudo scabies to humans.
Chirodiscoides caviae. A mite that lives like Listrophorus gibbus on the rabbit. It is mostly seen in the groin and armpits of the guinea pig and may cause itching and hair loss. It does not infect people.